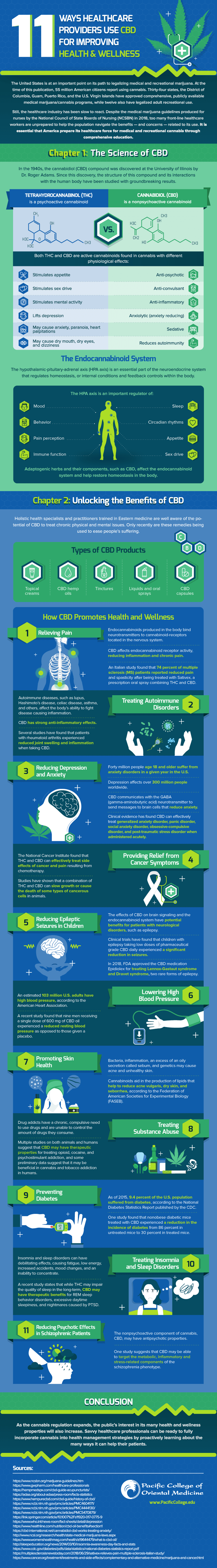
The United States is at an important point on its path to legalizing medical and recreational marijuana. At the time of this publication, 55 million American citizens report using cannabis. Thirty-four states, the District of Columbia, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands have approved comprehensive, publicly available medical marijuana/cannabis programs, while twelve also have legalized adult recreational use.
Still, the healthcare industry has been slow to react. Despite the medical marijuana guidelines produced for nurses by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) in 2018, too many front-line healthcare workers are unprepared to help the population navigate the benefits — and concerns — related to its use. It is essential that America prepare its healthcare force for medical and recreational cannabis through comprehensive education. Healthcare providers with an eye to the future are using CBD to improve health conditions of their patients.
To learn more, check out the infographic below created by Pacific College of Oriental Medicine.
Embed Code:
<p style="clear:both;margin-bottom:20px;"><a href="https://www.pacificcollege.edu//wp-content/uploads/2019/06/PCOM-11-Ways-Healthcare-Providers-Use-CBD-for-Improving-Patient-Health-Wellness.png"><img src="https://www.pacificcollege.edu//wp-content/uploads/2019/06/PCOM-11-Ways-Healthcare-Providers-Use-CBD-for-Improving-Patient-Health-Wellness.png" alt="11 Ways Healthcare Providers Use CBD to Improve Health & Wellness" style="max-width:100%;" /></a></p><p style="clear:both;margin-bottom:20px;"><a href="https://www.pacificcollege.edu" target="_blank">Pacific College of Oriental Medicine</a></p>Chapter 1: The Science of CBD
The cannabidiol (CBD) compound was discovered in the 1940s at the University of Illinois by Dr. Roger Adams. Since this discovery, the structure of this compound and its interactions with the human body have been studied with groundbreaking results.
One of the key factors in CBD studies involves differentiating CBD from tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). For instance, THC is a psychoactive cannabinoid, whereas CBD is nonpsychoactive. THC and CBD are also considered active cannabinoids that produce decidedly different physiological effects. THC stimulates appetite, sex drive, and mental activity, but it may also cause anxiety, paranoia, and heart palpitations. CBD, on the other hand, acts as an antipsychotic, an anticonvulsant, and an anti-inflammatory as well as an anxiety-reducing anxiolytic.
The Endocannabinoid System
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, or HPA axis, is regulated by the endocannabinoid system and is an essential part of the neuroendocrine system that regulates homeostasis, or internal conditions and feedback controls within the body. The axis acts as a vital regulator for mood, behavior, sleep, appetite, pain perception, and other key functions. Adaptogenic herbs and their components, like CBD, affect the endocannabinoid system and help restore homeostasis in the body.
Chapter 2: Unlocking the Benefits of CBD
Holistic health specialists and practitioners trained in Eastern medicine are well aware of CBD’s potential to treat chronic physical and mental issues. Only recently are these remedies being used to ease people’s suffering.
There are currently numerous CBD products on the market. These include topical creams, CBD hemp oils, tinctures, CBD capsules, liquids, and oral sprays. Regardless of product or form, there are several ways CBD promotes wellness and health in their users.
- 1. Relieving Pain
Endocannabinoids produced in the body bind neurotransmitters to cannabinoid receptors located in the nervous system. CBD affects this receptor activity, which reduces inflammation and chronic pain. For example, an Italian study found that 74% of multiple sclerosis patients reported reduced pain after treatment with Sativex, a prescription oral spray that combines THC and CBD.
- 2. Treating Autoimmune Disorders
Several autoimmune diseases like lupus, Hashimoto’s disease, celiac, or asthma affect the body’s ability to fight disease-causing inflammation. Due to CBD’s strong anti-inflammatory properties, it has been proven to reduce joint swelling and inflammation for patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
- 3. Reducing Depression and Anxiety
Forty million people age 18 and older suffer from anxiety disorders in a given year in the U.S., and depression affects over 300 million people worldwide. CBD communicates with the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter to send messages to brain cells to reduce anxiety. Clinical evidence has found CBD can effectively treat generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, and other similar conditions with proper administration.
- 4. Providing Relief from Cancer Symptoms
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) found that THC and CBD can effectively treat side effects of cancer and pain resulting from chemotherapy. Studies indicate that combining THC and CBD can slow growth or cause the death of certain cancerous cells in animals.
- 5. Reducing Epileptic Seizures in Children
CBD’s effects on brain signaling and the endocannabinoid system have potential benefits for patients with neurological disorders like epilepsy. Clinical trials have shown that children with epilepsy taking low doses of pharmaceutical grade CBD daily experienced a significant reduction in seizures.
- 6. Lowering High Blood Pressure
The American Heart Association (AHA) estimates 103 million American adults have high blood pressure. A recent study found that nine men receiving a single dose of 600 milligrams of CBD oil experienced a reduced resting blood pressure, compared to those given a placebo.
Are you interested in becoming a holistic nursing professional?
Visit the links below to explore our holistic nursing programs:
- 7. Promoting Skin Health
Bacteria, inflammation, an excess of an oily secretion called sebum, and genetics may cause acne and unhealthy skin. However, the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) states that cannabinoids aid in the production of lipids that help to lower acne vulgaris, dry skin, and seborrhea.
- 8. Treating Substance Abuse
Drug addicts have a chronic, compulsive need to use drugs and are unable to control the amount of drugs they consume. However, multiple studies suggest that CBD may contain therapeutic properties for treating opioid, cocaine, and psychostimulant addiction.
- 9. Preventing Diabetes
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that 9.4% of Americans suffer from diabetes. One study indicated that nonobese diabetic mice treated with CBD experienced a reduction in the incidence of diabetes, from 86% in untreated mice to 30% in treated mice.
- 10. Treating Insomnia and Sleep Disorders
Insomnia and sleep disorders can cause fatigue, low energy, increased accidents, and mood changes. A recent study states that while THC may impair long-term sleep quality, CBD may have therapeutic benefits for various sleep issues.
- 11. Reducing Psychotic Effects in Schizophrenic Patients
CBD may have antipsychotic properties. One study suggests that CBD may be able to target the metabolic, inflammatory, and stress-related components of the schizophrenia phenotype.
Conclusion
As the cannabis regulation expands, the public’s interest in its many health and wellness properties will also increase. Savvy healthcare professionals can be ready to fully incorporate cannabis into health management strategies by proactively learning about the many ways it can help their patients. Pacific College of Oriental Medicine offers the only fully accredited Medical Cannabis Certificate in the United States. Fill out the form at the top of this page to learn more about the Medical Cannabis Certificate.
Featured Posts: